Economy
SEC Publishes Rules for Exposure

By Dipo Olowookere
- New Rule
Asset Manager Code of Professional Conduct
1.1 General Principles of Conduct
Managers have the following responsibilities to their clients.
Managers must:
- Act in a professional and ethical manner at all times.
- Act for the benefit of clients.
- Act with independence and objectivity.
- Act with skill, competence, and diligence.
- Communicate with clients in a timely and accurate manner.
- Uphold the applicable rules governing capital markets.
1.2 Code of Professional Conduct
1.2.1 Obligation to clients
Managers must:
- Place client interests before their own.
- Preserve the confidentiality of information communicated by clients within the scope of the Manager–client relationship.
- Refuse to participate in any business relationship or accept any gift that could reasonably be expected to affect their independence, objectivity, or loyalty to clients.
1.2.2 Investment Process and Actions
Managers must:
- Use reasonable care and prudent judgment when managing client assets.
- Not engage in practices designed to distort prices or artificially inflate trading volume with the intent to mislead market participants.
- Deal fairly and objectively with all clients when providing investment information, making investment recommendations, or taking investment action.
- Have a reasonable and adequate basis for investment decisions.
- When managing a portfolio or pooled fund according to a specific mandate, strategy, or style:
- Take only investment actions that are consistent with the stated objectives and constraints of that portfolio or fund.
- Provide adequate disclosures and information so investors can consider whether any proposed changes in the investment style or strategy meet their investment needs.
- When managing separate accounts and before providing investment advice or taking investment action on behalf of the client:
- Evaluate and understand the client’s investment objectives, tolerance for risk, time horizon, liquidity needs, financial constraints, any unique circumstances (including tax considerations, legal or regulatory constraints, etc.) and any other relevant information that would affect investment policy.
- Determine that an investment is suitable to a client’s financial situation.
1.2.3 Trading
Managers must:
- Not act or cause others to act on material non-public information that could affect the value of a publicly traded investment.
- Give priority to investments made on behalf of the client over those that benefit the Managers’ own interests.
- Use commissions generated from client trades to pay for only investment-related products or services that directly assist the Manager in its investment decision making process, and not in the management of the firm.
- Maximize client portfolio value by seeking best execution for all client transactions.
- Establish policies to ensure fair and equitable trade allocation among client accounts.
1.2.4 Risk Management, Compliance and Support
Managers must:
- Develop and maintain policies and procedures to ensure that their activities comply with the provisions of this Code and all applicable legal and regulatory requirements.
- Appoint a compliance officer responsible for administering the policies and procedures and for investigating complaints regarding the conduct of the Manager or its personnel.
- Ensure that portfolio information provided to clients by the Manager is accurate and complete and arrange for independent third-party confirmation or review of such information.
- Maintain records for an appropriate period of time in an easily accessible format.
- Employ qualified staff and sufficient human and technological resources to thoroughly investigate, analyze, implement, and monitor investment decisions and actions.
- Establish a business-continuity plan to address disaster recovery or periodic disruptions of the financial markets.
- Establish a firm-wide risk management process that identifies, measures, and manages the risk position of the Manager and its investments, including the sources, nature, and degree of risk exposure.
1.2.5 Performance and Valuation
Managers must:
- Present performance information that is fair, accurate, relevant, timely, and complete. Managers must not misrepresent the performance of individual portfolios or of their firm.
- Use fair-market prices to value client holdings and apply, in good faith, methods to determine the fair value of any securities for which no independent, third-party market quotation is readily available.
1.2.6 Disclosures
Managers must:
- Communicate with clients on an ongoing and timely basis.
- Ensure that disclosures are truthful, accurate, complete, and understandable and are presented in a format that communicates the information effectively.
- Include any material facts when making disclosures or providing information to clients regarding themselves, their personnel, investments, or the investment process.
- Disclose the following:
- Conflicts of interests generated by any relationships with brokers or other entities, other client accounts, fee structures, or other matters.
- Regulatory or disciplinary action taken against the Manager or its personnel related to professional conduct.
- The investment process, including information regarding lock-up periods, strategies, risk factors, and use of derivatives and leverage.
- Management fees and other investment costs charged to investors, including what costs are included in the fees and the methodologies for determining fees and costs.
- The amount of any soft or bundled commissions, the goods and/or services received in return, and how those goods and/or services benefit the client.
- The performance of clients’ investments on a regular and timely basis.
- Valuation methods used to make investment decisions and value client holdings.
- Shareholder/unit holder voting policies.
- Trade allocation policies.
- Results of the review or audit of the fund or account.
- Significant personnel or organizational changes that have occurred at the Manager.
- Risk management processes.
2.0 Sundry Amendments
2.1 Amendment to Rule on Trading In Unlisted Securities – Inclusion of Debt Securities
- Existing Rule (a)
All Securities of unlisted public companies shall be bought, sold or transferred only by means of a system approved by the Commission and under such terms and conditions as the Commission may prescribe from time to time.
A slight amendment replacing the words “unlisted public” with “public unlisted” is being proposed. The new Rule will read as follows:
(a) All securities of public unlisted companies shall be bought, sold or transferred only by means of a system approved by the Commission and under such terms as the Commission may prescribe from time to time.
- New Rule (b) to provide as follows:
(b) All debt securities issued in Nigeria, i.e. issued by the Federal Government of Nigeria (“FGN”), Subnationals (State and Local Government), Supranational and Corporate entities, shall be bought, sold or transferred in the secondary market only through a SEC registered trading facility or Securities Exchange.
- A new Rule (c) to include regulation of trading in foreign currency securities of Nigerian entities listed in other jurisdictions is proposed as follows:
(c) All exchange of debt securities traded (including foreign currency securities of Nigerian entities listed in other jurisdictions e.g. Eurodollar bonds) in the Nigerian capital market shall be executed on or reported to a SEC-registered Securities Exchange or trading facility.
- Existing Rule (b) which provides that:
No person shall buy, sell or otherwise transfer securities of an unlisted public company except through the platform of a registered securities exchange established for the purpose of facilitating over-the-counter trading of securities.
To be slightly amended and renumbered as Rule (d) to compel trading of securities of public companies on SEC-registered platforms only, is proposed as follows:
(d) No person shall buy, sell or otherwise transfer securities of a public unlisted company or government agency except through the platform of a SEC-registered securities exchange or trading facility established for the purpose of facilitating over-the-counter trading of securities.
- Existing Rule (c) which provides that:
Any unlisted public company, director, company secretary, registrar, broker/dealer or such other persons who facilitates the buying, selling or transfers of the securities of an unlisted public company otherwise than through the platform of a registered securities exchange, shall be liable to a penalty of not less than N100, 000 in the first instance and not more than N5, 000 for every day the infraction continues.
The existing Rule (c) as outlined above to be slightly amended and renumbered as Rule (e) to read as follows:
- Any public unlisted company, director, company secretary, registrar, broker/dealer or such other persons who facilitate the buying, selling or transfer of the securities of a public unlisted company or government agency otherwise than through the platform of a SEC-registered securities exchange or trading facility shall be liable to a penalty of not less than N100,000 in the first instance and not more than N5,000 for every day of default.
2.2 Review of Capital Requirement for Sub-Brokers
- Existing Rule 67(1)(j) which provides that Corporate Sub-Broker (to show) evidence of minimum paid-up capital of N1million.
Amendment of Rule 67(1)(j) to provide that Corporate Sub-Broker (to show) evidence of minimum paid-up capital of N10million.
- Existing Schedule I, Part B(5) which reflects N5million as minimum paid up capital requirement for Corporate Sub-Brokers
Amendment of Schedule I, Part B(5) to reflect N10million as minimum paid up capital requirement for Corporate Sub-Brokers
- Existing Rule 67(2)(a)(ii) which provides that Individual Sub-Broker (to show) evidence of minimum net worth of N500,000.00
Amendment of Rule 67(2)(a)(ii) to provide that Individual Sub-Broker (to show) evidence of minimum net worth of N1million.
- Existing Schedule I, Part B(6) which reflects N500,000.00 as minimum net worth requirement for Individual Sub-Brokers.
Amendment of Schedule I Part B(6) to reflect N1million as minimum net worth requirement for Individual Sub-Brokers.
Related articles across the web
Economy
5 Secrets to Unlocking Business Success in Nigeria

Nigeria’s business environment continues to evolve rapidly, presenting both opportunities and challenges for entrepreneurs. In recent years, digital transformation has become a cornerstone for growth, with businesses across various sectors embracing new technologies to remain competitive. For those looking to thrive in this dynamic landscape, understanding market trends and leveraging innovative strategies is crucial.
Whether it’s a startup or an established enterprise, success often hinges on adaptability, strategic planning, and the ability to seize emerging opportunities. Even in sectors like entertainment and sports, where trends shift quickly, businesses must stay agile to maintain relevance. For instance, some entrepreneurs are exploring new revenue streams such as online platforms, including activities like แทงบอล ufabet, which have gained popularity due to their accessibility and appeal to a broad audience.
The Nigerian Business Landscape in 2025
The Nigerian business landscape in 2025 is marked by rapid technological adoption, increased competition, and a growing demand for digital solutions. Sectors such as fintech, e-commerce, and digital marketing have seen significant growth, driven by a young, tech-savvy population. Entrepreneurs are now leveraging digital tools to streamline operations, reach wider audiences, and improve customer engagement. The government’s push for economic diversification has also created new opportunities in agriculture, manufacturing, and renewable energy. However, businesses must navigate challenges such as regulatory hurdles, infrastructure gaps, and fluctuating market conditions. Despite these obstacles, the resilience and creativity of Nigerian entrepreneurs continue to drive innovation and growth.
Why Strategic Planning is Essential
Strategic planning is the foundation of any successful business. It involves setting clear goals, identifying resources, and developing actionable steps to achieve objectives. In Nigeria’s competitive market, businesses that invest time in strategic planning are better equipped to anticipate challenges, capitalize on opportunities, and adapt to changing circumstances. Effective planning also helps businesses allocate resources efficiently, minimize risks, and maximize returns. Entrepreneurs should regularly review and update their strategies to stay aligned with market trends and customer needs. By doing so, they can maintain a competitive edge and position their businesses for long-term success.
Leveraging Digital Tools for Growth
Digital tools have revolutionized the way businesses operate in Nigeria. From cloud-based software to social media platforms, these tools enable businesses to automate processes, enhance communication, and reach a global audience. For example, e-commerce platforms allow businesses to sell products online, while digital marketing tools help them target specific customer segments and measure campaign effectiveness. Additionally, mobile payment solutions have made transactions faster and more secure, improving customer satisfaction. By embracing digital transformation, businesses can increase efficiency, reduce costs, and expand their market reach.
Building a Strong Team Culture
A strong team culture is vital for business success. It fosters collaboration, boosts morale, and drives innovation. Nigerian entrepreneurs should prioritize creating a positive work environment where employees feel valued and motivated. This can be achieved by promoting open communication, recognizing achievements, and providing opportunities for professional development. A cohesive team is more likely to overcome challenges, generate creative solutions, and contribute to the overall growth of the business. Investing in team-building activities and leadership training can further strengthen the organizational culture.
Overcoming Common Challenges
Nigerian businesses face a range of challenges, including access to finance, regulatory compliance, and competition. Access to capital remains a major hurdle for many entrepreneurs, particularly startups and small businesses. Regulatory compliance can also be complex and time-consuming, requiring businesses to stay informed about changing laws and policies. Additionally, intense competition in key sectors can make it difficult for businesses to differentiate themselves. To overcome these challenges, entrepreneurs should seek support from government agencies, industry associations, and financial institutions. Building strong networks and partnerships can also provide valuable resources and guidance.
Adapting to Market Trends
Adapting to market trends is essential for staying relevant in Nigeria’s fast-paced business environment. Entrepreneurs must stay informed about emerging trends, consumer preferences, and technological advancements. This can be achieved by conducting market research, attending industry events, and monitoring competitor activities. By anticipating changes and responding proactively, businesses can seize new opportunities and mitigate potential risks. For example, the growing demand for sustainable products and services presents opportunities for businesses to innovate and differentiate themselves.
Importance of Financial Management
Effective financial management is critical for business sustainability and growth. It involves budgeting, cash flow management, and financial reporting. Nigerian entrepreneurs should prioritize financial literacy and seek professional advice when needed. Proper financial management enables businesses to track performance, make informed decisions, and secure funding. It also helps businesses comply with regulatory requirements and build trust with stakeholders. By maintaining sound financial practices, entrepreneurs can ensure the long-term viability of their businesses.
Future Outlook for Nigerian Entrepreneurs
The future outlook for Nigerian entrepreneurs is promising, with continued growth expected in key sectors such as technology, agriculture, and renewable energy. The government’s focus on economic diversification and infrastructure development is likely to create new opportunities for businesses. Additionally, the rise of digital platforms and e-commerce is expected to drive innovation and expand market reach. Entrepreneurs who embrace change, invest in digital transformation, and prioritize strategic planning are well-positioned to succeed in Nigeria’s evolving business landscape.
Economy
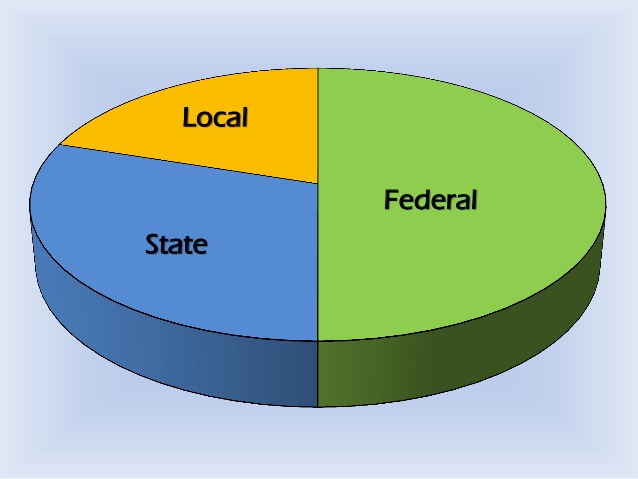
FG, States, LGs Share N1.928trn From November 2025 Revenue
By Adedapo Adesanya
The federal government, states and the Local Government Councils have received a sum of N1.928 trillion from the revenue generated in November 2025 by the federation.
According to a statement by the Federation Account Allocation Committee (FAAC), the earnings were shared at the December 2025 FAAC meeting held in Abuja, where the total distributable revenue comprised statutory revenue of N1.403 trillion, Value Added Tax (VAT) revenue of N485.838 billion, and Electronic Money Transfer Levy (EMTL) revenue of N39.646 billion.
It was disclosed that total gross revenue of N2.343 trillion was available in the month of November 2025, with N84.251 billion deducted for cost of collection and N330.625 billion for total transfers, interventions, refunds and savings.
FAAC stated that gross statutory revenue of N1.736 trillion was received for the month of November 2025, lower than the N2.164 trillion received in the month of October 2025 by N427.969 billion.
Gross revenue of N563. 042 billion was available from VAT in November 2025, lower than the N719.827 billion available in the month of October 2025 by N156.785 billion.
In November 2025, Excise Duty increased moderately while Petroleum Profit Tax (PPT), Hydrocarbon Tax (HT), CIT on Upstream Activities, Companies Income Tax (CIT), CGT and SDT, Oil & Gas Royalties, Import Duty, CET Levies, Value Added Tax (VAT), Electronic Money Transfer Levy (EMTL) and Fees recorded substantial decreases.
From the N1.928 trillion total distributable revenue, the federal government got N747.159 billion, the state governments received N601.731 billion, and the local councils shared N445.266 billion, while N134.355 billion was given to benefiting states as 13 per cent of mineral derivation.
On the N1.403 trillion distributable statutory revenue, the national government received N668.336 billion, the 36 states got N338.989 billion, and the LGAs received N261.346 billion, and N134.355 billion shared as 13 per cent of mineral revenue.
In addition, from the N485.838 billion distributable VAT revenue, the central government got N72.876 billion, the state governments shared N242.919 billion, and the local councils shared N170.043 billion.
Further, N5.947 billion was taken by the federal government from the N39.646 billion EMTL, the states shared N19.823 billion, and the councils received N13.876 billion.
Economy
Golden Capital, FrieslandCampina Trigger 0.04% Loss at NASD OTC Exchange

By Adedapo Adesanya
The duo of Golden Capital Plc and FrieslandCampina Wamco Nigeria Plc weakened the NASD Over-the-Counter (OTC) Securities Exchange by 0.04 per cent on Monday, December 15.
This pulled down the NASD Unlisted Security Index (NSI) by 1.37 points to 3,599.06 points from last Friday’s 3,600.43 points and the market capitalisation lost N820 million to close at N2.153 billion compared with the preceding session’s N2.154 trillion.
Golden Capital Plc depleted by 94 Kobo to end at N8.51 per share compared with N9.45 per share and FrieslandCampina Wamco Nigeria Plc depreciated by 63 Kobo to sell at N59.60 per unit versus N60.23 per unit.
During the session, the volume of securities traded at the session slumped by 98.4 per cent to 600,402 units from 37.4 million units, the value of securities fell by 99.8 per cent to N7.8 million from N4.9 billion, and the number of deals shed 36.4 per cent to 21 deals from 33 deals.
At the close of trades, Infrastructure Credit Guarantee Company (InfraCredit) Plc remained the most traded stock by value with a year-to-date sale of 5.8 billion units valued at N16.4 billion, followed by Okitipupa Plc with 178.9 million units transacted for N9.5 billion, and MRS Oil Plc with 36.1 million units worth N4.9 billion.
InfraCredit Plc was also the most traded stock by volume on a year-to-date basis with 5.8 billion units worth N16.4 billion, trailed by Industrial and General Insurance (IGI) Plc with the sale of 1.2 billion units for N420.3 million, and Impresit Bakolori Plc with 537.0 million units traded for N524.9 million.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism9 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking7 years ago
Banking7 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn